
The composition of the agate will play a role in the diaphaneity and translucency of the specimen, with less impurities resulting in higher transparency/translucency and more impurities hindering the ability for light to pass through.
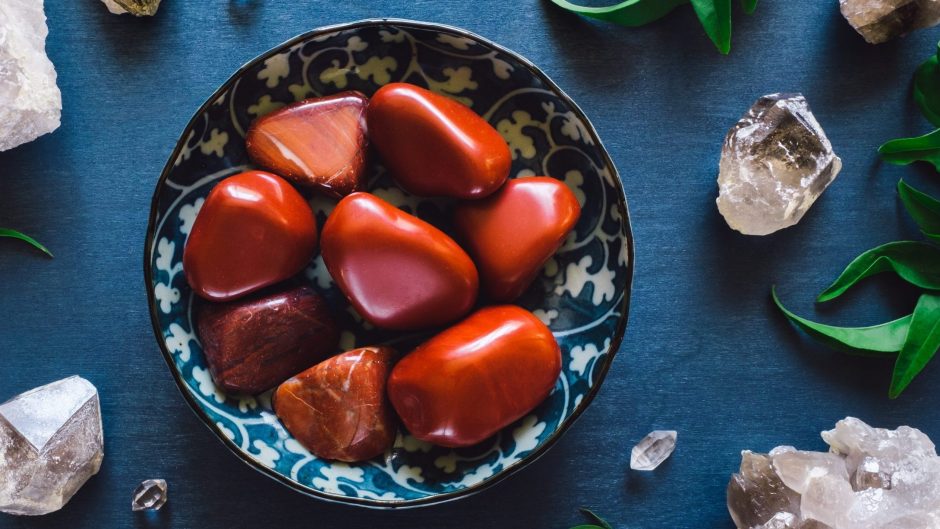
Some agates are diaphanous, meaning the image on the opposite side of the agate is clear and not very distorted, however in most cases translucency is the best classification for agate. When light cannot pass through the surface of the substance, it’s classified as being opaque. When light can pass through the substance but in a distorted fashion, the substance is categorized as translucent. When light can pass through a substance without distortion or disturbance, the substance is considered transparent. Diaphaneity is described as the way light interacts with the surface of a substance. The easiest visible identifier for dissociation between agate and jasper is the mineral’s “diaphaneity”. Visible Differences Between Agate and Jasper Most often, the impurities present determine the coloration of the deposit following solidification, however other factors can play a role in the color of what is now considered a jasper. The fluids then crystallize around the particles/impurities, resulting in a cementation process. In most cases, jasper will occur when silica-rich fluids permeate throughout a soft sedimentation or volcanic debris deposit. Like agate it may form in a huge variety of colors, and is often multi-colored.Ī slab of colorful mookaite jasper from Australia. Jasper is a term that can be applied to an opaque variety of chalcedony (light does not pass through it) The opaqueness is due to a much larger amount of impurities mixed with silica/quartz. These agate formations occur throughout the world in locations where volcanic activity has created these environments, explaining why agate nodules and geodes can be found on every continent. Mineral-rich water then made its way into the hollow cavity and provided the necessary minerals were present, agate could then form within the cavity.

Eventually the gas escaped through the rock following the rock solidifying and cracking. They moved their way up through the rock as it was still in a viscous state. These bubbles within the rock formed as a result of rapid gas formation from expansion of volatile components. Nodular or geodic agate formations occur in bubbles within the host rock that were created during volcanic activity. Agate can also form within cavities of fossilized remains, explaining why many fossils are agatized. In some cases this can result in concentric banding within a nodule, or layered formations within cracks (seams, vugs, veins, etc.) of rocks. Depending on impurities present during formation, the agate will exhibit varied coloration as the impurities work their way into the crystal lattice. This deposition occurs molecule by molecule, forming tightly packed fibrous microcrystalline quartz crystals that line the contact walls of the cavity.

It forms when a silica-rich, gelatin-like solution fills an open cavity within rock and begins to deposit crystals evenly along the walls. Some people insist to strictly use the term agate to describe translucent chalcedony with circular banding patterns, but this stricter definition is not in general use.Ī banded Laguna Agate from Ojo Laguna, Mexico Like chalcedony, it may form in a huge variety of colors and patterns. The term agate may generally be used to describe any form of chalcedony that is translucent (light will pass through it). Dependent on impurities present during formation, chalcedony can form in a wide variety of colors including red, yellow, green, blue, purple, grey, white and numerous color hues in between.Ĭhalcedony is quite hard, being a 7 on the Mohs Hardness Scale, which makes sense considering quartz is the benchmark mineral for a 7.
#TYPES OF JASPER FREE#
When free from impurities, chalcedony is colorless and transparent. Both quartz and moganite have the same chemical formula SiO2 (silicon dioxide) but different crystal structures. Microcrystalline meaning the crystals are microscopic and cannot be observed by the naked eye.

Agate is any type of chalcedony which is translucent, while jasper is any type of chalcedony which is opaque.Ĭhalcedony is any microcrystalline variety of silica composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. Chalcedony is a broad term to describe a microcrystalline form of silica.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
